Workstation Ergonomics
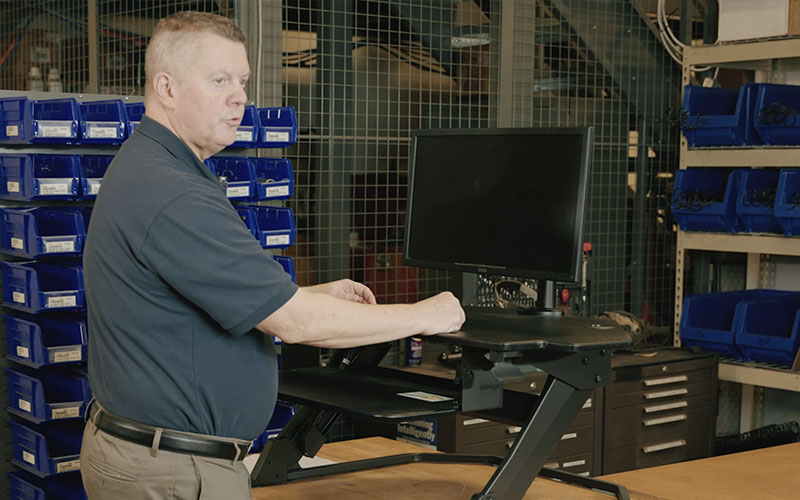

Leading companies are integrating ergonomics into all of their operations. And it’s no wonder when you take a look at the benefits of an effective ergonomics process, ranging from reduced worker fatigue and increased productivity, to increased health and employee engagement. Watch as A&M Industrial's Mike Hamilton demonstrates the basics of workstation ergonomics and how you can implement ergonomic principles at your workplace.
Applying Ergonomics to Enhance Employee Wellbeing
What exactly is ergonomics? In the simplest terms, ergonomics is designing a job or workstation to fit the worker and make the work performed safer, more comfortable, and more efficient. In doing so, productivity is increased, creating a win-win for both a company and its employees. Essentially, ergonomics is the science a 'fitting' a worker and their work.
The 3 Fundamental Principles Of Ergonomics
- Maintain Neutral Postures: Neutral postures are postures where the body is aligned and balanced while either standing or sitting, keeping joints aligned and placing minimal stress on the body. Neutral postures minimize the stress applied to bones, muscles, and nerves.
- Reduce Excessive Force: reducing excessive force requirements on the body reduces worker fatigue and the risk of MSDs (Musculoskeletal Disorders). MSDs include Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Tendinitis (shoulder), Epicondylitis (elbow), Trigger Finger and Muscle Strains.
- Keep Things Easy To Reach: keeping frequently used items within arm's reach reduces the need to stand, stretch, or bend the body, reducing risk of injury or muscle strain.
Ergonomic Computer Workstations
When implementing ergonomic computer workstations, we are trying to arrange or adjust the computer workstation to promote healthy neutral postures:
-
Head/neck 'in line' with torso
-
Head/neck/trunk facing forward 'in line'
-
Torso vertical or slightly reclined, 90° or greater
-
Back fully supported by chair lumbar
-
Shoulders relaxed – not elevated
-
Elbows close to the body – not extended
-
Forearms parallel to the floor
-
Wrists/hands/forearms straight, not bent
-
Femur/thighs parallel to the floor
-
Thighs have clearance under desk
-
Legs/feet have clearance
-
Feet flat on floor or footrest
12 Point Checklist For Ergonomic Comfort
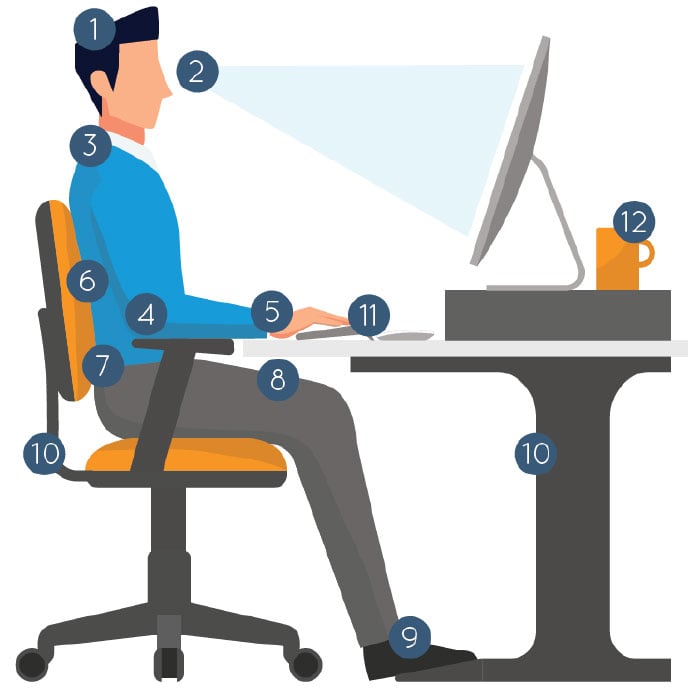
-
Head: Upright and over shoulders. Looking straight ahead at screen or monitor, not tilted upward or downward.
-
Eyes: Looking slightly downward, about a 30° range from the horizontal line of sight, without bending the neck. Room lighting should allow you to see the screen without strain or glare.
-
Shoulders: Relaxed, never hunched.
-
Elbows: Bent at 90°, forearms resting horizontally on chair armrests.
-
Wrists: Straight, relaxed in a neutral position.
-
Back: Supported by a chair with a backrest that promotes the natural curve of the lower back, from the lower back to your shoulder blades.
-
Hips: Slightly higher or level with the knees, thighs horizontal with a 90° to 110° angle at hip.
-
Thighs: Legs supported on the seat, with two to three inches of space behind knee.
-
Feet: Fully supported and flat on the floor. If that position is not possible without support, place your feet fully on a footrest.
-
Chair and Desk: Height adjusted so that keyboard, mouse and work surface are level with elbow height.
-
Laptop: Elevated laptop and wireless keyboard for optimal ergonomic comfort.
-
Frequent Breaks: Take a break every 30 minutes or so to stand, stretch, walk around and allow your eyes to rest from staring at the screen. Set an alarm to ensure you remember.
Want To Implement Ergonomics At Your Business?
Contact us to arrange an on-site or virtual ergonomics assessment. Simply complete and submit the request form, below!


